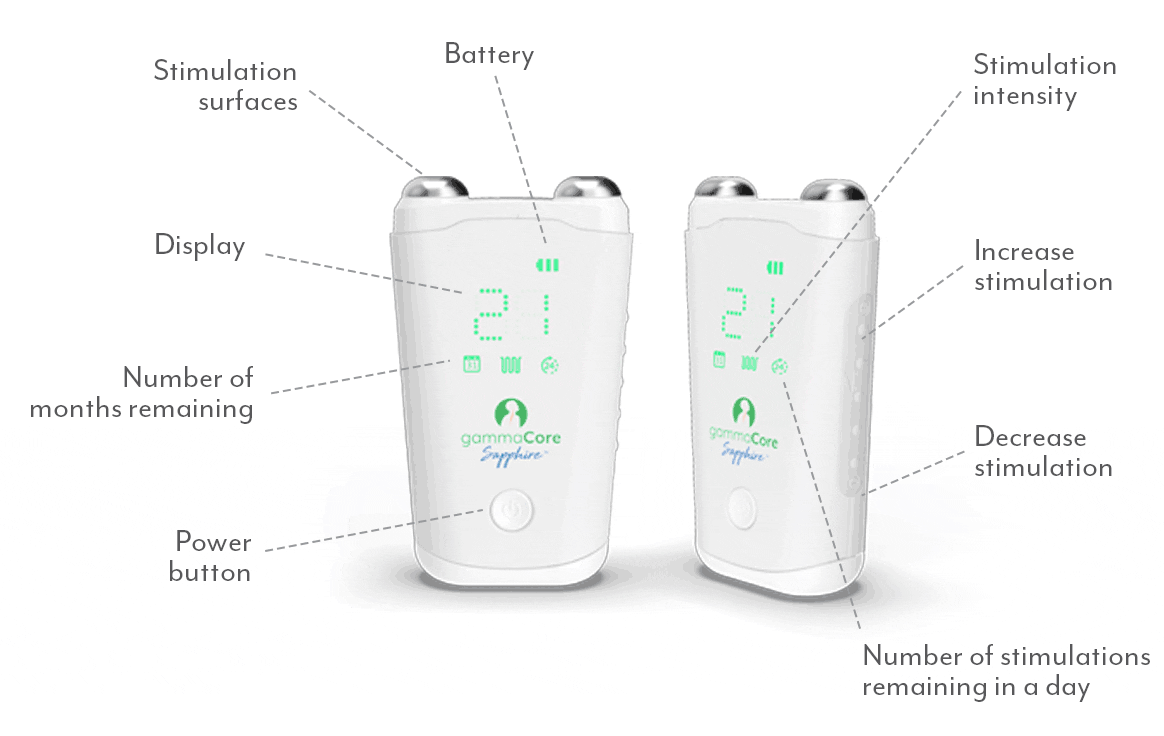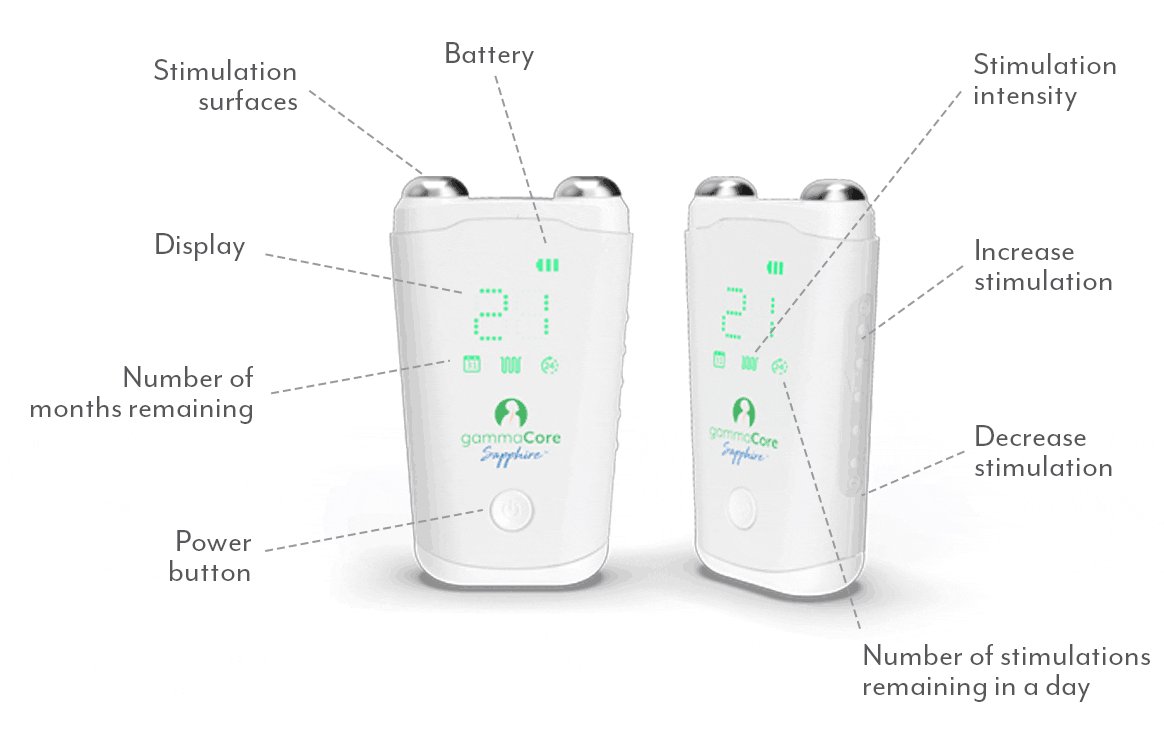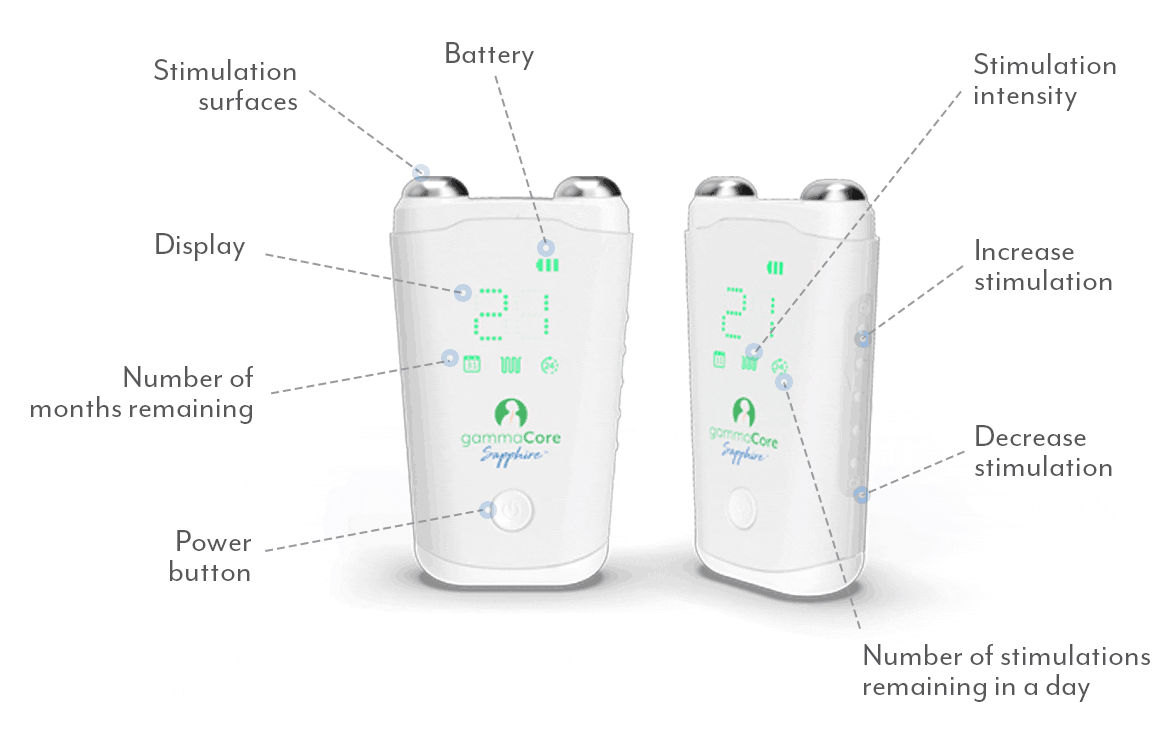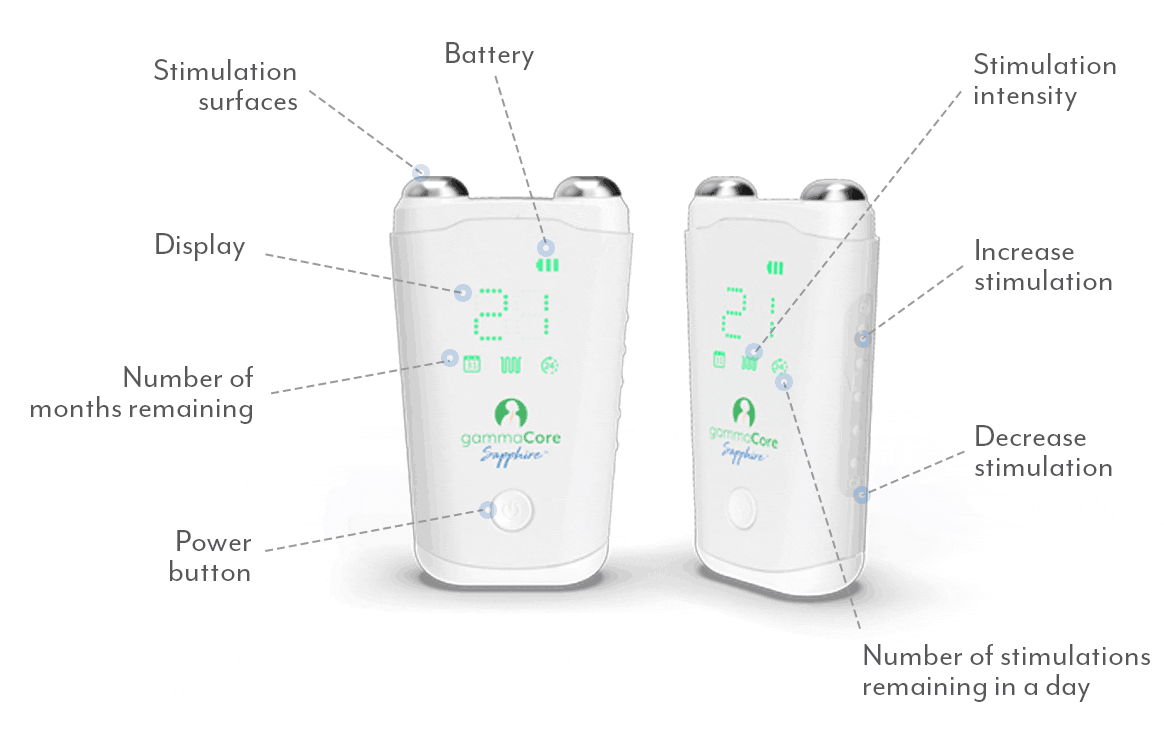
A proven safe and well-tolerated non-drug treatment
For migraine headache1
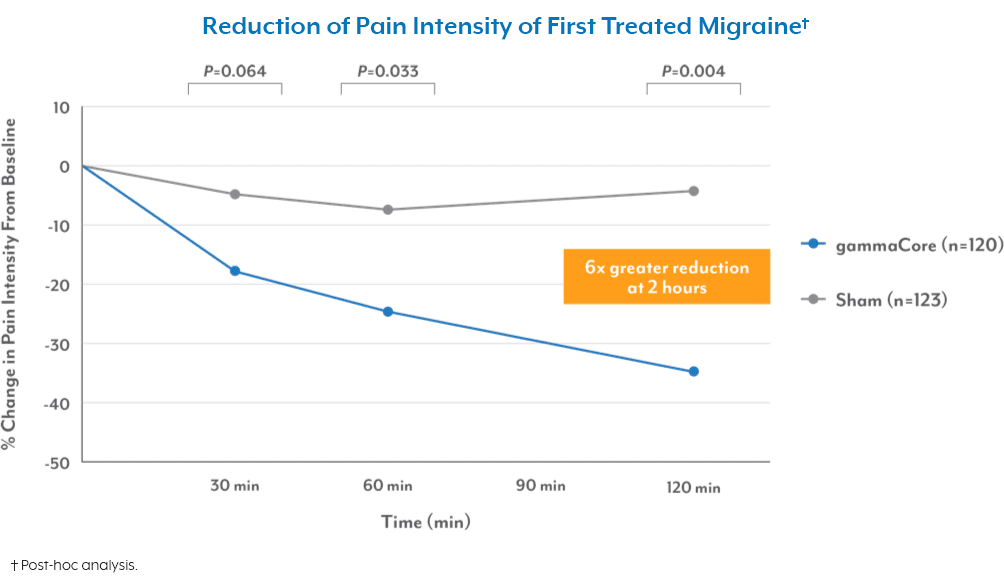
In PRESTO, the most common device-related adverse events (AEs) ≥2% were application-site discomfort (2.5% vs 0.8%), application-site erythema (0% vs 2.4%), application-site pain (0% vs 2.4%), and dizziness (0% vs 1.6%) in the gammaCore (nVNS) and sham arm, respectively. Most AEs were mild and transient and occurred primarily during administration.
PRESTO Adverse Device-Related Events (Safety Population)1
For cluster headache prevention2

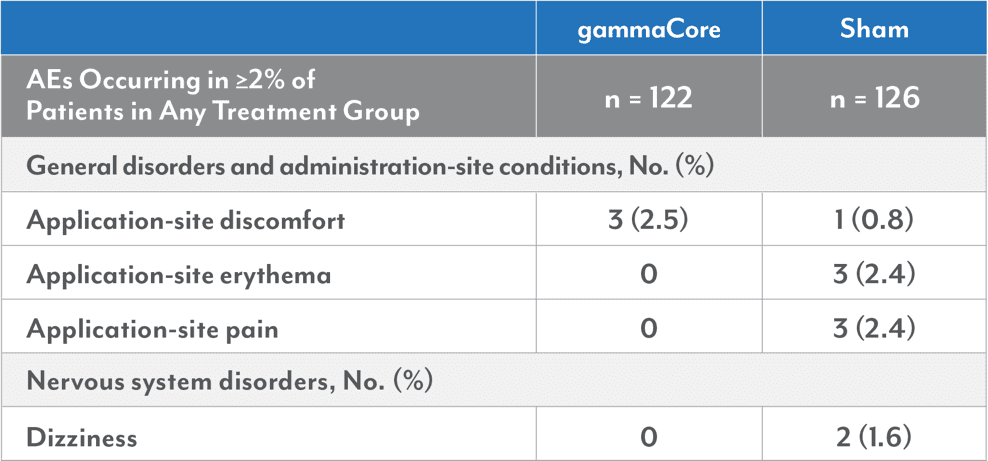
- In the PREVA study, most AEs were considered mild or moderate. The most common AEs in any treatment group were cluster headache attacks, headache, nasopharyngitis, dizziness, oropharyngeal pain, and neck pain. No serious AEs were considered gammaCore related
PREVA Safety and Tolerability*
*Included ≥1 AE determined by causality assessment to be related to treatment.
For episodic cluster headache1,3

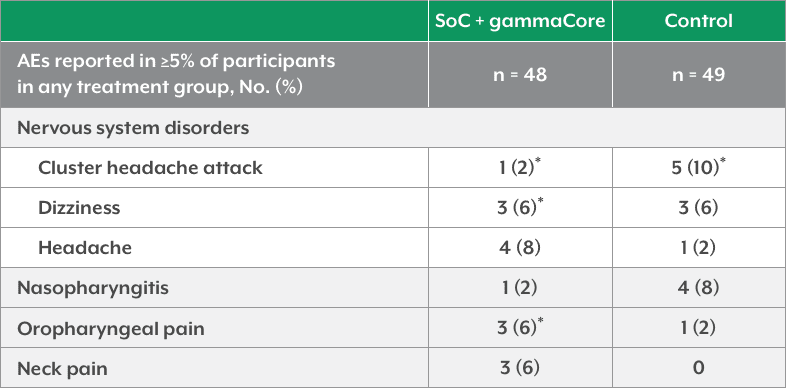
- In ACT1, the most common adverse device-related events were mild and transient, and occurred primarily during administration
ACT1 Adverse Device-Related Events1,3 (Occurring in ≥5% of Patients in Any Treatment Group)
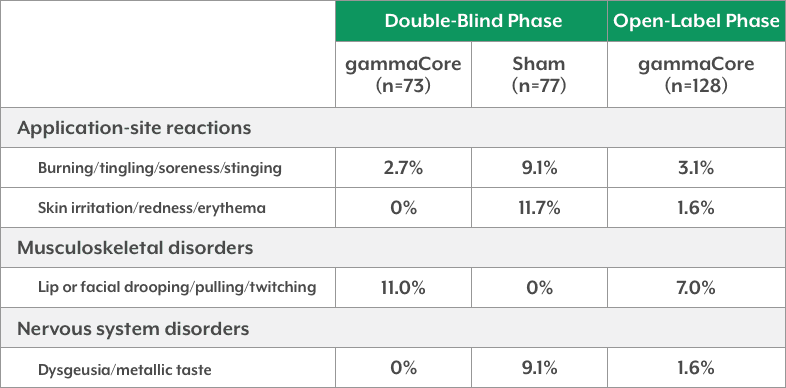

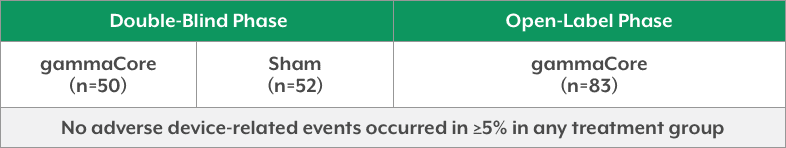
- In ACT2, no adverse device-related events were observed in ≥5% of patients in any treatment group1,4
ACT2 Adverse Device-Related Events1,4 (Occurring in ≥5% of Patients in Any Treatment Group)
References: 1. gammaCore Instructions for Use. Basking Ridge, NJ: electroCore, Inc.; 2018. 2. Gaul C, Diener HC, Silver N, et al; PREVA Study Group. Non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation for PREVention and Acute treatment of chronic cluster headache (PREVA): a randomised controlled study. Cephalalgia. 2016;36(6):534-546. 3. Silberstein SD, Mechtler LL, Kudrow DB, et al; ACT1 Study Group. Non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation for the acute treatment of cluster headache: findings from the randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled ACT1 study. Headache. 2016;56(8):1317-1332. 4. Goadsby PJ, de Coo IF, Silver N, et al; ACT2 Study Group. Non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation for the acute treatment of episodic and chronic cluster headache: a randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled ACT2 study. Cephalalgia. 2018;38(5):959-969.